Of those affected, about 4.3 million people live in Guizhou and Hunan provinces, with the rest are in Hubei, Chongqing, Jiangxi and Zhejiang, according to the ministry. As of 9 a.m. Monday, about 4.03 million people were in need of government assistance, the report said.
Drought in China leaves nearly 6 million lacking water
The Climate Is Set to Change 'Orders of Magnitude' Faster Than at Any Other Time in the Past 65 Million Years
A new paper in the journal Science finds that climate change is now set to occur at a pace "orders of magnitude more rapid" than at any other time in the last 65 million years. That breakneck speed may mean extinction for species that cannot keep up.
For example, the paper's authors Noah S. Diffenbaugh and Christopher B. Field of Stanford write, consider the global cooling that took place beginning some 52 million years ago. That change was of a greater magnitude than even the worst-case global-warming projections for the 21st century.
‘Frack Gag’ Bans Children From Talking About Fracking, Forever
When drilling company Range Resources offered the Hallowich family a $750,000 settlement to relocate from their fracking-polluted home in Washington County, Pennsylvania, it came with a common restriction. Chris and Stephanie Hallowich would be forbidden from ever speaking about fracking or the Marcellus Shale.
But one element of the gag order was all new. The Hallowichs’ two young children, ages 7 and 10, would be subject to the same restrictions, banned from speaking about their family’s experience for the rest of their lives.
Tar Sands Oil Has Been Leaking Into Alberta For 10 Weeks And No One Knows How To Stop It
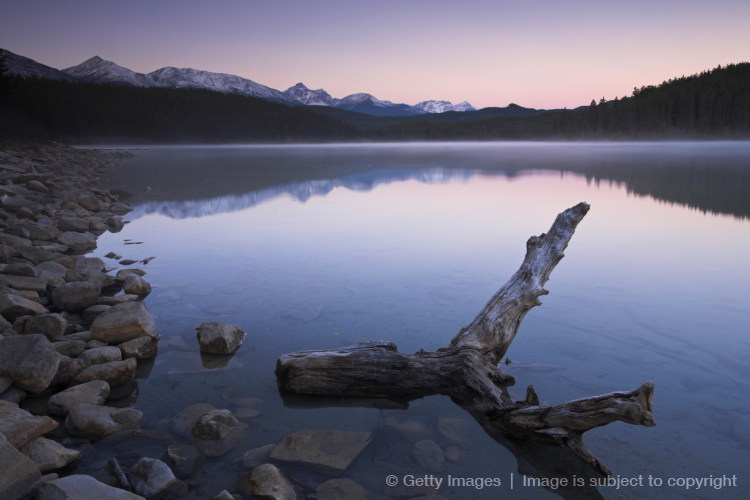

Indeed, recent documents show that the company responsible for the spill estimates that the tar sands oil has been leaking into the ecosystem for around four months, based on winter snow coverage.
Climate study predicts a watery future for New York, Boston and Miami
 More than 1,700 American cities and towns – including Boston, New York, and Miami – are at greater risk from rising sea levels than previously feared, a new study has found.
More than 1,700 American cities and towns – including Boston, New York, and Miami – are at greater risk from rising sea levels than previously feared, a new study has found.
By 2100, the future of these 1,700 locations will be "locked in" by greenhouse gas emissions built up in the atmosphere, the analysis published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences on Monday found.
Potential well water contaminants highest near natural gas drilling, UT Arlington study says
 A new study of 100 private water wells in and near the Barnett Shale showed elevated levels of potential contaminants such as arsenic and selenium closest to natural gas extraction sites, according to a team of researchers that was led by UT Arlington associate professor of chemistry and biochemistry Kevin Schug.
A new study of 100 private water wells in and near the Barnett Shale showed elevated levels of potential contaminants such as arsenic and selenium closest to natural gas extraction sites, according to a team of researchers that was led by UT Arlington associate professor of chemistry and biochemistry Kevin Schug.
The results of the North Texas well study were published online by the journal Environmental Science & Technology Thursday. The peer-reviewed paper focuses on the presence of metals such as arsenic, barium, selenium and strontium in water samples. Many of these heavy metals occur naturally at low levels in groundwater, but disturbances from natural gas extraction activities could cause them to occur at elevated levels.
Halliiburton pleads guilty to destroying Gulf spill evidence
Halliburton Co has agreed to plead guilty to destroying evidence related to the 2010 Gulf of Mexico oil spill, the U.S. Department of Justice said on Thursday.
The government said Halliburton's guilty plea is the third by a company over the spill and requires the world's second-largest oilfield services company to pay a maximum $200,000 statutory fine.
Halliburton also agreed to three years of probation and to continue cooperating with the criminal probe into the April 20, 2010, explosion of the Deepwater Horizon drilling rig.
Truthout investigation: Fracking in the Ocean Off the California Coast
The Pacific Ocean may be the next frontier for fracking technology.
A Truthout investigation has confirmed that federal regulators approved at least two hydraulic fracturing, or "fracking," operations on oil rigs in the Santa Barbara Channel off the coast of California since 2009 without an updated environmental review that critics say may be required by federal law.
The offshore fracking operations are smaller than the unconventional onshore operations that have sparked nationwide controversy, but environmental advocates are still concerned that regulators and the industry have not properly reviewed the potential impacts of using modern fracking technology in the Pacific outer continental shelf.
Cancer Concerns With Colorado's Drilling, Fracking Boom
 A former president of the Colorado Medical Society calls the current hydraulic fracturing boom in the state’s oil and gas industry an “experiment in motion” for the public at large.
A former president of the Colorado Medical Society calls the current hydraulic fracturing boom in the state’s oil and gas industry an “experiment in motion” for the public at large.
One that could lead to higher rates of cancer and other illnesses over the next 10 to 15 years.
Dr. Michael Pramenko, a Grand Junction family physician, says he isn’t as worried about acute cases of exposure to carcinogens in “fracking” fluid – although he has treated a patient who accidently guzzled cancer-causing benzene. Pramenko says he is more concerned with long-term exposure from tainted water.
More Articles...
Page 49 of 157

 Environmental News Archive
Environmental News Archive