The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is wading into tense territory with a new rule essentially making the agency an abortion provider, facing the wrath of GOP lawmakers and likely legal challenges.
The VA has already started providing abortions to pregnant veterans and VA beneficiaries in limited circumstances set out in the rule, which took effect when it was published on Sept. 9.
The landmark rule quickly raised questions about the infrastructure to handle demand, and the legal consequences of performing the services in red states where abortion is banned or severely restricted.
But the VA has shown no signs of backing down from its rule — which it says will cover about 1,000 abortion procedures per year — and advocates are hailing it as a major step forward in health care for veterans.
More...
 Military Glance
Military Glance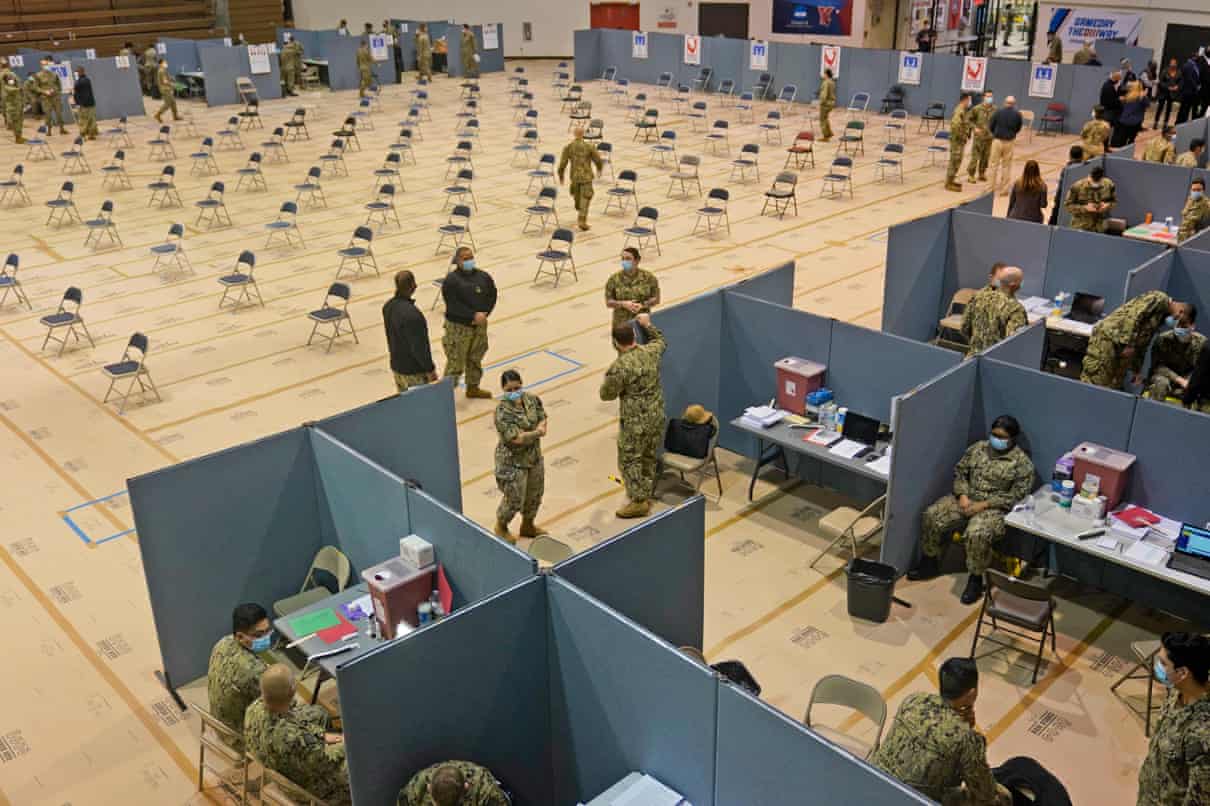 Reluctance to be vaccinated for Covid-19 is now rife in the
Reluctance to be vaccinated for Covid-19 is now rife in the  The U.S. military on Wednesday acknowledged it was unsure about how to address white nationalism and other extremism in its ranks, and announced plans for military-wide stand-downs pausing regular activity at some point in the next 60 days to tackle the issue.
The U.S. military on Wednesday acknowledged it was unsure about how to address white nationalism and other extremism in its ranks, and announced plans for military-wide stand-downs pausing regular activity at some point in the next 60 days to tackle the issue.